With Broadcom’s licensing changes to VMware, many organizations are rethinking their virtualization strategies. Some are moving away from proprietary hypervisors toward open alternatives like Proxmox VE, while others are seizing the opportunity to modernize their application layer with OpenShift, Red Hat’s enterprise Kubernetes platform.
So how do you choose between OpenShift vs Proxmox? Both are powerful, but serve different purposes. Proxmox delivers control over infrastructure, while OpenShift orchestrates applications. Let’s dive into how they differ to help you decide which best fits your modernization goals.
What Is Proxmox VE?
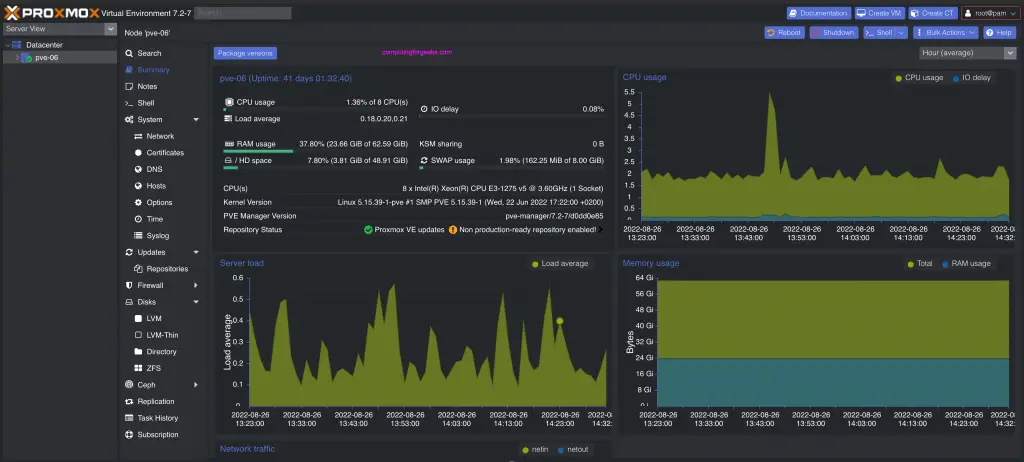
Proxmox Virtual Environment (VE) is an open-source platform for running virtual machines and Linux containers (LXC) on a single, integrated system. Built on Debian GNU/Linux, it combines KVM virtualization, container management, and software-defined storage and networking in one interface.
Proxmox is ideal for organizations leaving VMware behind, offering similar enterprise capabilities without licensing restrictions.
Key features include:
- KVM for high-performance VM hosting.
- LXC for lightweight, OS-level containers.
- Ceph, ZFS, and LVM-thin storage options.
- Corosync and Proxmox Cluster File System for high availability.
What Is OpenShift?
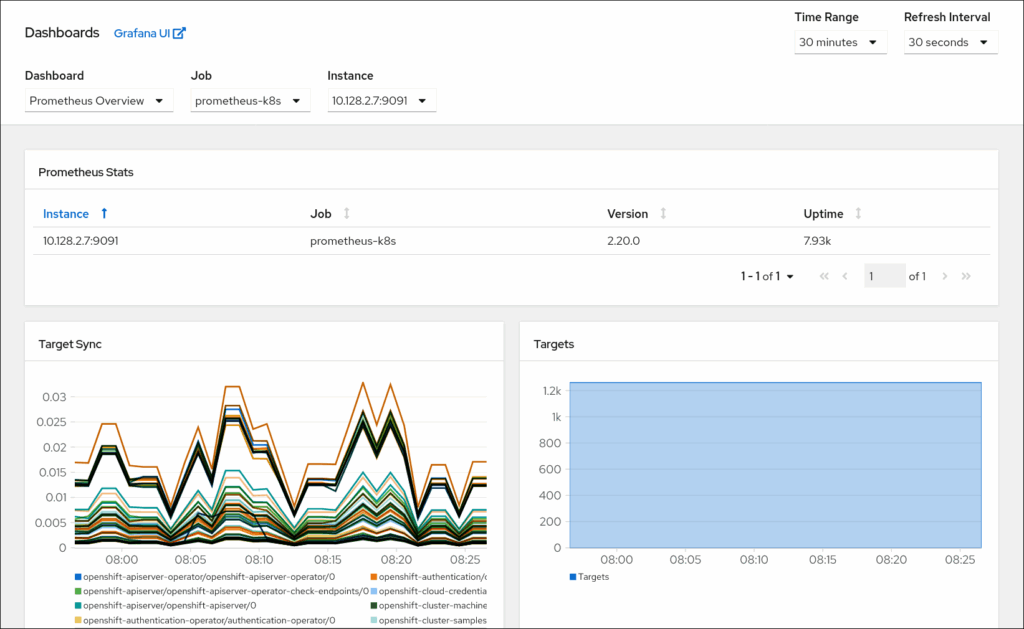
OpenShift Container Platform is Red Hat’s Kubernetes distribution designed to deploy and scale containerized applications across clouds and data centers. Each cluster runs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) and uses Kubernetes with CRI-O for container runtime.
OpenShift extends Kubernetes with:
- CI/CD pipelines and integrated build automation.
- OperatorHub for lifecycle management.
- Built-in image registry and routing layer.
- Enterprise security and compliance via SELinux and RBAC.
While Proxmox focuses on infrastructure, OpenShift focuses on delivering modern, cloud-native applications.
How Do Their Architectures Differ?
Proxmox runs the infrastructure layer: hypervisors, containers, and storage. OpenShift operates above it, orchestrating workloads and automating DevOps processes.
Feature |
Proxmox VE | OpenShift |
Core Function |
Virtualization and container hosting | Application orchestration |
Base OS |
Debian GNU/Linux | Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS |
Management Tools |
Web GUI, CLI, REST API | oc CLI, web console, Operators |
Storage |
Ceph, ZFS, NFS, LVM | Persistent Volumes, CSI drivers |
Users |
System administrators | Developers and DevOps teams |
How Do They Handle Virtualization?
Proxmox VE natively manages both VMs and containers. Administrators can:
- Run any OS with QEMU/KVM.
- Deploy LXC containers for fast, efficient workloads.
- Use Proxmox Backup Server for deduplicated backups and restores.
OpenShift focuses on containers but includes OpenShift Virtualization to run VMs alongside pods. This hybrid approach lets teams migrate gradually from legacy virtualization while adopting DevOps practices.
How Is Networking Managed?
Proxmox VE
- Uses Linux bridges, VLAN tagging, and bonded interfaces.
- Includes a cluster-aware firewall with per-VM rules.
- Offers full control for private or hosted environments.
OpenShift
- Uses software-defined networking (SDN) for automated pod connectivity.
- Supports NetworkPolicies, Ingress Controllers, and Service Mesh.
- Enforces multi-tenant isolation through RBAC and SELinux.
Proxmox manages host-level networking; OpenShift manages service-to-service traffic between containers.
How Is Storage Managed?
Proxmox is hardware-centric. OpenShift is application-centric.
Proxmox VE
- Integrates directly with Ceph for distributed, fault-tolerant storage.
- Supports ZFS, LVM-thin, and NFS for flexible configurations.
- Offers snapshots, replication, and automated backup scheduling.
OpenShift
- Abstracts storage through Persistent Volumes (PVs) and StorageClasses.
- Uses the OpenShift Data Foundation for scalable block and object storage.
- Automatically provisions storage through Kubernetes APIs.
How Do They Handle High Availability and Scaling?
Proxmox scales infrastructure capacity. OpenShift scales applications and services.
Proxmox VE
- Uses Corosync for quorum and failover.
- Automatically restarts workloads on healthy nodes.
- Expands easily by adding nodes to a cluster.
OpenShift
- Scales applications horizontally through Kubernetes autoscaling.
- Includes multicluster management for hybrid or multi-cloud operations.
- Balances workloads automatically across infrastructure.
How Are Backup and Recovery Managed?
Proxmox VE includes Proxmox Backup Server for encrypted, incremental backups with deduplication and scheduled restore points.
OpenShift integrates backup through Operators or third-party tools that protect cluster data and persistent volumes. It’s flexible but requires more setup compared to Proxmox’s built-in backup system.
How Easy Are They to Use and Automate?
Proxmox simplifies infrastructure management. OpenShift simplifies continuous delivery.
Proxmox VE
- Intuitive Web GUI for managing VMs, storage, and networking.
- Command-line tools (qm, pct, pvesh) and a REST API for scripting.
- Works with Ansible and Terraform for automation.
OpenShift
- Developer-friendly web console and oc CLI.
- Operator Framework, CI/CD pipelines, and GitOps workflows built in.
- Enables self-service deployment under centralized governance.
Looking to migrate without overlap costs?
Migration shouldn’t drain your budget. With HorizonIQ’s 2 Months Free, you can move workloads, skip the overlap bills, and gain extra time to switch providers without double paying.
Get 2 Months FreeHow Do OpenShift vs Proxmox Costs Compare?
Proxmox simplifies infrastructure management. OpenShift simplifies continuous delivery.
- Proxmox VE is fully open source, licensed under AGPL, with optional paid support. It is ideal for service providers and enterprises seeking predictable costs.
- OpenShift is subscription-based, including Red Hat’s enterprise support, certified updates, and security assurance.
Who Should Use Each Platform?
Use Case |
Proxmox VE | OpenShift |
Replacing VMware |
Native HA clustering and Ceph integration make it a strong alternative. | Supports gradual VM-to-container transition via OpenShift Virtualization. |
Private Cloud Hosting |
Excellent for on-prem or managed service providers. | Ideal for enterprises building modern app platforms. |
Hybrid or Multi-Cloud |
Manual network and storage federation possible. | Native hybrid and multicluster tools included. |
DevSecOps and CI/CD |
Integrates via Ansible or Terraform. | CI/CD pipelines and GitOps are native. |
Budget and Licensing |
Free and open source. | Commercial subscription with full vendor support. |
How Do You Choose Between OpenShift vs Proxmox?
If your goal is to control infrastructure—VMs, containers, and storage—Proxmox VE provides a complete, open platform with predictable costs. It’s an excellent replacement for VMware environments or for building private clouds that need transparency and flexibility.
If your goal is to deliver applications faster, OpenShift provides a turnkey platform for DevOps teams with enterprise security and automation built in. It’s best suited for large organizations managing microservices and multi-cloud workloads.
In many cases, the strongest approach is using both together. Proxmox as the underlying compute layer on bare-metal or manually provisioned VMs, and OpenShift as the application orchestration layer.
To learn more about deploying OpenShift on Proxmox, check out Deploy OpenShift OKD on Proxmox VE or bare-metal (user-provisioned).
How Can HorizonIQ Help?
At HorizonIQ, we help businesses modernize infrastructure and transition away from proprietary systems.
Our Proxmox Managed Private Cloud replaces costly VMware environments with high-availability clustering, Ceph storage, and predictable pricing.
With HorizonIQ, you gain:
- Expert-led migration planning and management.
- Fully managed Proxmox environments with transparent pricing.
- Compass, our management portal for monitoring, support, and scaling from one dashboard.
By combining open-source flexibility with enterprise reliability, HorizonIQ gives you a cloud strategy that grows on your terms, without lock-in or compromise.