Month: July 2025

Proxmox vs vSphere: Which Virtualization Platform is Right for Your Business?
Why Are Businesses Rethinking vSphere in 2025?
VMware has long been the enterprise gold standard for virtualization, but that status is being challenged. Following Broadcom’s acquisition, vSphere users are facing rising costs, rigid licensing (such as 72-core minimums), and shrinking support for smaller deployments. For companies needing flexibility, affordability, and control, Proxmox has emerged as a powerful open-source alternative.
At HorizonIQ, we believe in the value of choice.
We will continue to support VMware for customers who rely on it while providing options for those exploring what’s next. Whether you’re migrating away from vSphere, expanding your infrastructure, or simply comparing paths forward, we’re here to help you evaluate the right platform for your business.
Let’s break down the key differences between Proxmox vs vSphere. Not just as platforms, but through the lens of how we’ve architected Proxmox for real-world performance, predictable cost, and hands-on manageability.

What’s the Architectural Difference Between Proxmox VE and VMware vSphere?
| Hypervisor Architecture | Proxmox VE | VMware vSphere |
| Hypervisor Type | KVM (Type-1) + LXC | ESXi (Type-1) |
| Host OS | Debian Linux | Proprietary VMkernel |
| Cluster Manager | Built-in | vCenter Server (Add-on VM) |
| Kernel Updates | Live kernel patching | Scheduled via vCenter |
Takeaway:
Proxmox is open, flexible, and Linux-native—ideal for DevOps teams and businesses wanting transparency and control. vSphere, by contrast, relies on proprietary components that limit customization.
How Do Proxmox and vSphere Compare for VM and Container Management?
| VM Management | Proxmox VE | vSphere |
| VM Support | Full VMs + LXC Containers | Full VMs only |
| Snapshots | RAM, disk, and state | RAM, disk, and state |
| Templates | VMs + Containers | VMs only |
| Guest Tools | QEMU Guest Agent | VMware Tools |
| Console Access | NoVNC, SPICE, xterm.js | HTML5, VNC, VMRC |
Why It Matters:
Proxmox’s native container support (via LXC) makes it ideal for lightweight, high-density workloads. With HorizonIQ’s managed Proxmox clusters, businesses can run containers alongside VMs with full isolation and resource throttling. No add-ons required.
What’s the Difference Between Proxmox and vSphere Networking Capabilities?
| Networking | Proxmox VE | vSphere |
| Virtual Switches | Linux Bridge, Open vSwitch | vSwitch, vDS |
| Layer 2 Isolation | Zones + Vnets | Port Groups |
| SDN | Built-in (VXLAN, OVS) | NSX (Add-on) |
| Firewalls | Host- and VM-level | NSX (Add-on) |
Edge Insight:
With HorizonIQ’s Proxmox Managed Private Cloud, SDN and firewalling are built-in, not bolted on. That means less complexity, lower cost, and faster provisioning, especially when our team configures and manages it all for you.
How Do Proxmox and vSphere Handle High Availability and Live Migration?
| High Availability Feature | Proxmox VE | vSphere |
| HA | Yes (native) | Yes |
| Live Migration | QEMU-based | vMotion |
| Storage Migration | Supported | Storage vMotion |
| Fault Tolerance | Not supported | Supported |
| DRS | Available (via add-ons) | Built-in |
Context:
vSphere edges ahead with fault tolerance and DRS as standard, but Proxmox’s HA features (when backed by HorizonIQ’s redundant Ceph storage) are more than enough for most real-world use cases.
How Do Storage and Backup Options Compare in Proxmox vs vSphere?
| Storage Feature | Proxmox VE | vSphere |
| Shared Storage | Ceph, ZFS, NFS, GlusterFS | NFS, iSCSI, FC, vSAN |
| Pooling/DRS | Manual | Policy-driven (SDRS) |
| Backup | Proxmox Backup Server (native) | 3rd Party (e.g., Veeam) |
| DR | Limited | Supported via Zerto |
| Thin Provisioning | Yes | Yes |
| Deduplication | Yes | Yes |
Built for Backup:
HorizonIQ extends native Proxmox backups with automated retention, off-site replication, and Compass integration for visibility and control. No third-party licenses required.
Which Platform Offers Better Automation and DevOps Support: Proxmox or vSphere?
| Automation Feature | Proxmox VE | vSphere |
| REST API | Yes | Yes |
| Infrastructure as Code | Ansible, Terraform | Ansible, Terraform |
| CLI Scripting | Bash, Python, native tools | PowerCLI, govc |
| Hooks/Scripts | Pre/Post Start/Stop | Lifecycle-limited |
Developer-Approved:
Proxmox gives you direct control over automation and orchestration. HorizonIQ builds on that by providing reusable templates, auto-scaling hooks, and full API access ready for CI/CD or GitOps workflows.
How Do Proxmox and vSphere Integrate with Kubernetes and Public Cloud?
| Ecosystem Feature | Proxmox VE | vSphere |
| Containers | Native LXC | Requires Tanzu Add-On |
| Kubernetes | KubeVirt, Rancher | Tanzu Add-On |
| Public Cloud | Manual Integration | VMware Cloud on AWS/Azure |
Open by Design:
Proxmox enables you to build flexible, multi-cloud or hybrid strategies without vendor lock-in. At HorizonIQ, we manage the heavy lifting—from multi-region deployments to Kubernetes integration—so you stay focused on innovation.
Which Virtualization Platform Is More Cost-Effective: Proxmox or vSphere?
vSphere comes with licensing, subscription, and add-on fees (like NSX or vCenter), while Proxmox VE is open-source with optional paid support. Here’s how we simplify that equation:
- No licensing headaches
- Month-to-month pricing
- 70% average cost savings
- All-inclusive: storage, firewalls, Compass, and support
Which Is Right for Your Infrastructure?
| Ideal For | Proxmox VE | vSphere |
| Budget-Conscious SMBs | Yes | No |
| Full-Stack Freedom | Yes | No |
| Enterprise Fault Tolerance | No | Yes |
| Regulatory Compliance | Yes (via HorizonIQ) | Yes |
| Container & VM Mix | Yes | Partial (Tanzu required) |
| AI/ML Workloads | Yes | Limited (hardware dependent) |
| DevOps/Automation | Yes | Yes |
Proxmox shines when you need:
- Cost-effective, high-performance private cloud
- Flexible VM + container orchestration
- Support without a VMware tax
- Simple scaling across geographies
With HorizonIQ’s Managed Private Cloud, you get all that plus SLAs, enterprise-grade storage, and 24/7 support.
Looking to migrate without overlap costs?
Migration shouldn’t drain your budget. With HorizonIQ’s 2 Months Free, you can move workloads, skip the overlap bills, and gain extra time to switch providers without double paying.
Get 2 Months FreeWhy Choose HorizonIQ to Run Proxmox?
Whether you’re consolidating infrastructure, modernizing your virtualization stack, or looking for more predictable pricing, HorizonIQ delivers.
- First US-based fully managed Proxmox private cloud
- Ceph-backed HA clusters and dedicated hardware tiers
- Proactive monitoring and 100% uptime SLA
- Compass portal for visibility, control, and cost optimization
- Supported by a team that acts as an extension of yours
Still Running on vSphere?
Our engineers will meet you where you are. If you’re ready to switch, we’ll manage the entire migration. If you plan to stay on VMware, we’ll optimize your stack for performance, resilience, and cost. Contact us today.
Explore HorizonIQ's
Managed Private Cloud
LEARN MORE
Stay Connected

If your business runs workloads across public cloud, private cloud, and on-prem infrastructure, securing your hybrid environment should be a top priority. Hybrid cloud gives you flexibility and scalability, but it also introduces new security risks.
According to Gigamon’s 2025 Hybrid Cloud Security Survey, 91% of Security and IT leaders acknowledge they’re forced to make compromises by sacrificing visibility and relying on siloed, poor-quality data.
With AI and the growing threat of ransomware attacks, many are being forced to rethink their hybrid cloud strategies. In this guide, you’ll learn what hybrid cloud security is, why it matters to your organization, and how to protect your data and applications using proven best practices and tools.
What Is Hybrid Cloud Security and Why Does It Matter?
Hybrid cloud security refers to the practices, technologies, and policies that are put in place to protect data, applications, and infrastructure within a hybrid cloud environment.
In this approach, resources are comprised of public clouds (i.e., AWS, Azure, or GCP), private clouds, and on-premises data centers.
Hybrid delivers scalability and agility to businesses but also allows them to maintain data security controls. But without a cohesive security strategy, it also introduces serious risks.
Multi-Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud Security: What’s the Difference?
Hybrid cloud security is frequently more centralized, based on traffic and data flow controls between cloud and on-prem. Multi-cloud security necessitates broader controls in order to tackle one-of-a-kind risks across different vendor platforms.
| Security Type | Description | Focus |
Hybrid Cloud Security |
Protects workloads across private and public cloud environments | Integration and consistency |
Multi-Cloud Security |
Secures assets across multiple public cloud providers | Provider diversity and interoperability |
What Are the Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Security?
- Data Control: Sensitive data will remain on-prem or in private cloud environments.
- Regulatory Compliance: Makes compliance with industry standards more manageable by segmenting where and how data is stored.
- Scalability with Security: Public cloud is used for non-sensitive tasks or traffic spikes for better overall security.
- Disaster Recovery: The public cloud can also act as a failover target, improving resilience.
- Cost Efficiency: Blend of low-cost public cloud and secure private infrastructure minimizes cost without compromising security.
What Are the Biggest Challenges of Securing Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid environments are complex. Security teams must navigate gaps in visibility, policy enforcement, and identify management across different platforms. Without a unified strategy, even strong efforts can fall short.
| Challenge | Description |
Shared Responsibility |
Clarifying roles between the organization and cloud providers |
Incident Handling |
Coordinating across multiple environments with varying visibility |
Application Security |
Managing consistent policies and remediation across deployment models |
Identity & Access Management |
Handling identity sprawl, role confusion, and machine-to-machine authorization |
Compliance |
Ensuring audit-readiness and uniform governance across decentralized platforms |
Supply Chain Risk |
Vetting third-party tools and infrastructure for vulnerabilities |
Data Protection |
Maintaining encryption and access control policies are consistent |
Visibility and Monitoring |
Gaining full-stack observability across disparate platforms and environments |
How Is Hybrid Cloud Security Designed?
Securing hybrid infrastructure requires a thoughtfully designed architecture, which includes:
- Zero Trust Security: All access requests are authenticated, no matter where they originate.
- Microsegmentation: Divides networks into isolated areas to limit lateral movement.
- Firewalls & DMZs: Multilayered protection between cloud and on-prem.
- Encryption: All data in transit and at rest will be encrypted.
- Monitoring and Logging: Real-time visibility through centralized SIEM solutions.
What Are the Core Components of Hybrid Cloud Security?
| Component Type | Examples |
Physical Controls |
Locked data centers, surveillance systems, backup power infrastructure |
Technical Controls |
Encryption, orchestration, zero-trust access, endpoint protection |
Administrative Controls |
Training, compliance policies, audits, incident response procedures |
How Do Organizations Maintain Governance and Compliance?
- Regulatory Mapping: Identify which workloads fall under which jurisdiction (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR).
- Audit Logs: Centralize and make immutable logs.
- Data Residency Enforcement: Keep secured data on-premises or in private places.
- Vendor SLAs: Include compliance guarantees in third-party contracts.
What Are the Best Practices for Hybrid Cloud Security?
- Encrypt Everything: Encrypt all connections using SSL/TLS and encrypt data in rest to minimize exposure.
- Zero Trust, Always: Grant access only as needed and always verify.
- Standardize IAM: Use a unified identity management system across all clouds.
- Restrict Access Using Least Privilege: Minimize scopes for machines as well as users.
- Segment the Network: Prevent unauthorized lateral movement.
- Automate Configuration Management: Prevent drift and reduce misconfiguration risk.
- Invest in Observability: Real-time SIEM, threat intelligence, and anomaly detection.
- Train Your Personnel: Security culture is all about people.
These best practices work best when used together, creating a layered defense that spans every environment your business touches.
What Tools and Technologies Enable Hybrid Cloud Security?
| Tool/Technology | Purpose |
VPNs |
Secure communication between cloud and on-prem |
Firewalls |
Protect perimeter and internal traffic |
CASBs |
Enforce security policies between users and cloud apps |
SIEM |
Centralized logging and real-time threat detection |
IDPS |
Prevent DDoS, malware, and intrusion attempts |
MFA |
Add layers to authentication processes |
DLP |
Prevent sensitive data from leaking or being misused |
CWPPs |
Protect workloads, containers, and serverless deployments |
How Can Organizations Prepare for the Future of Hybrid Cloud Security?
- Zero-Trust Expansion: Adopt identity-first security and dynamic access models.
- Cloud-Native Security: Embrace tooling that is container- and serverless-specific.
- Edge Security: Protecting data at the edge through gateways and secure protocols.
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning in Security: Quickly automate threat detection, analysis, and prevention.
- Integrated Security Management: Select products that bring together visibility and control.
Hybrid cloud delivers agility and flexibility, but security requires an integrated, cautious method.
Businesses can secure their hybrid environments without sacrificing performance or increasing risk by using a multi-layered security architecture across infrastructure types and enforcing least-privilege access. Automation for compliance and the right tools and processes further strengthen this approach.
Hybrid cloud security is not a public or private choice. It’s about building a single, effective strategy that combines both and prepares your organization for whatever’s next.
How Does HorizonIQ Strengthen Hybrid Cloud Security?
Hybrid cloud security depends on protecting workloads across private, public, and on-prem environments. HorizonIQ’s hybrid cloud solutions help businesses maintain control without sacrificing scalability.
Secure Private Infrastructure
HorizonIQ’s single-tenant private cloud and bare metal servers provide physical isolation for sensitive workloads to keep regulated data off shared platforms. This supports compliance goals (HIPAA, PCI DSS, ISO 27001) and simplifies enforcement of encryption, access control, and data residency policies.
Controlled Public Cloud Integration
Rather than isolating businesses from the public cloud, HorizonIQ securely connects to it:
HorizonIQ Connect, powered by Megaport, provides private, high-speed links to AWS, Azure, GCP, and over 280 other cloud providers. These private connections bypass the public internet, reducing attack surfaces while maintaining control over traffic flows.
This approach supports zero-trust networking, microsegmentation, and consistent policy enforcement across environments.
Enterprise Networking and Built-In Protection
HorizonIQ’s multi-carrier IP Transit delivers high-performance networking with built-in redundancy and DDoS protection. Dedicated firewall options and role-based access controls at the infrastructure level help secure both internal and external traffic.
HorizonIQ offers the physical controls, network security, and centralized management needed for secure hybrid environments. Organizations can confidently protect sensitive data in private infrastructure while scaling into public clouds, without compromising security.
Ready to secure your hybrid cloud? Let’s talk about your custom solution.
Explore HorizonIQ's
Managed Private Cloud
LEARN MORE
Stay Connected
Top 10 VMware Alternatives: Complete Virtualization Guide for All Business Sizes
Is VMware Still the Right Choice for Your Virtualization Needs?
If you’ve been relying on VMware for your virtualization needs, you’re not alone. It’s been the go-to for enterprise IT for years, holding about 44% of the market. But things are shifting in 2025, and you might be feeling the pinch.
Broadcom’s acquisition of VMware in late 2023 has led to massive price hikes (some as high as 2–3x, or even 10x in cases like AT&T’s). New licensing rules, like 72-core minimums for vSphere, are also pushing many to look elsewhere. In fact, according to Gartner’s Peer Community, 74% of IT leaders are currently exploring VMware alternatives. If you’re rethinking your virtualization strategy, you’re in the right place.
At HorizonIQ, we work closely with organizations navigating this shift, especially those prioritizing predictability, compliance, and cost control in their infrastructure stack. I’ll walk you through why so many are moving away from VMware, break down the top alternatives for 2025, and give you tailored recommendations based on your company’s size and infrastructure.
Whether you’re running a small IT shop or managing a global enterprise, you’ll get clear comparisons, real-world use cases, and practical advice to help you pick the right VMware alternative.
What Is VMware?
Since 1999, VMware has been a leading provider of virtualization and cloud computing software. At its core, VMware allows you to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server, maximizing hardware efficiency and flexibility.
Each VM operates with its own operating system and applications, just like a physical server. The most common components used in enterprise environments include:
Platform |
Description |
ESXi |
A Type-1 hypervisor installed directly on hardware to manage virtual machines. |
vSphere |
VMware’s suite of tools, including vCenter Server, for managing ESXi hosts and VMs. |
vMotion |
Enables live migration of running VMs between physical servers with no downtime. |
High Availability (HA) |
Automatically restarts VMs on other hosts in case of a hardware failure. |
VMware Cloud |
Offers hybrid and multi-cloud capabilities, such as VMware Cloud on AWS. |
Tanzu |
VMware’s Kubernetes platform for containerized application deployment. |
For years, VMware has been considered the gold standard in enterprise virtualization due to its rich feature set, robust performance, and reliability.
However, with dramatic price hikes and vendor lock-in concerns following the Broadcom Acquisition, many have begun to express their concerns.
Why Are Companies Seeking VMware Alternatives?
Organizations are starting to reassess long-standing tools like VMware, not necessarily because the technology isn’t strong, but because the environment around it has changed. You may have leaned on VMware’s vSphere platform, powered by the ESXi hypervisor and vCenter management, for its rock-solid features like live migration (vMotion), high availability, and robust VM management.
Its hybrid-cloud options, like VMware Cloud on AWS, and container support through Tanzu keep have attracted privacy-first organizations for years. Here are some of the top reasons customers are considering VMware alternatives:
Skyrocketing Costs
As previously mentioned, since Broadcom took over, VMware’s licensing fees have spiked. Many smaller businesses are also being hit hard by the loss of affordable bundles like vSphere Essentials Plus.
Feature Overload
If you don’t need advanced tools like Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), you’re likely overpaying for bells and whistles you don’t use. Adding to the frustration, Broadcom’s EMEA CTO recently brushed off customer complaints about the VMware price hikes by claiming that customers simply aren’t using it properly to get VMware Cloud Foundation’s full advantages.
Cloud and Hybrid Needs
As you adopt hybrid cloud or containerized setups, you’ll need platforms that play nicely with tools like Kubernetes or public clouds. Something VMware struggles with without expensive add-ons like Tanzu.
Complexity
VMware’s feature-packed ecosystem demands specialized skills and hefty hardware, which can overwhelm smaller teams or inflate costs.
Vendor Lock-In
VMware’s proprietary setup can trap you, making it tough to integrate with other platforms or migrate away.
Niche Workloads
If you’re running GPU-heavy virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), many are finding better performance on specialized platforms that offer optimized GPU virtualization and higher VDI density out of the box.
How Do the Best VMware Alternatives Compare?
| Alternative | Key Features | Scalability & Performance | Licensing/Cost Model | Support & Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Hyper-V |
Type-1 hypervisor, Windows integration, Shielded VMs | Enterprise-grade; supports large VMs (48TB RAM) | Included with Windows Server | Microsoft support, integrates with Azure, AD, System Center |
Proxmox VE |
Open-source, KVM + LXC, web UI, clustering, Ceph | Scales from labs to clusters; near bare-metal KVM performance | Free; paid support optional | Community and enterprise support; integrates with Ceph, NFS, APIs |
Nutanix AHV |
Type-1 HCI hypervisor, Prism UI, one-click operations | Scalable via node expansion; ideal for large enterprise setups | Included with Nutanix HCI | Enterprise support; integrates with Prism, AWS/Azure |
XCP-ng |
Open-source Xen-based, managed via Xen Orchestra | Multi-host pools; solid Xen performance | Free; optional Vates support | Xen tools, VMware migration tools; commercial and community support |
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization |
KVM-based, OpenShift console, Ansible automation | Scales to hundreds of VMs; runs Linux + Windows alongside containers | Subscription-based, cost-effective for Linux shops | Red Hat support, integrates with RHEL, Ansible, OpenShift |
OpenStack |
Open-source IaaS, modular services (Nova, Neutron, Cinder, etc.) | Highly scalable; supports multi-region clouds and massive deployments | Free; staffing and support costs | Large community; vendor support available (e.g. Red Hat, Canonical) |
Harvester |
Open-source HCI platform, KubeVirt, Rancher UI, VM + container support | Small to medium clusters; scales via Rancher-managed clusters | Free; community-supported | Integrates with Rancher, Kubernetes, Longhorn; community support |
XenServer |
VDI-optimized, GPU support, integrates with Citrix VDI | Supports 960 logical processors/host; excels in VDI | Free trial, paid for premium features | Citrix support, smaller ecosystem, Windows-only XenCenter |
SUSE Linux Enterprise |
KVM/Xen support, integrates with Rancher, Secure Boot | Scales on modern hardware; ideal for SAP and Linux-heavy workloads | Subscription-based | SUSE support, integrates with Rancher, standard virtualization protocols |
Oracle VirtualBox |
Free Type-2 hypervisor, GUI, snapshot/clones | Limited scalability; best for dev/test | Free; optional commercial Extension Pack | Community support, supports OVF/OVA; limited enterprise tools |
What Are the Top VMware Alternatives?
The best VMware alternative will come down to your use case and budget, but we recommend considering the following:
1. Microsoft Hyper-V
If you’re already invested in Windows, Microsoft Hyper-V is a no-brainer. Built into Windows Server, this Type-1 hypervisor supports both Windows and Linux VMs, with features like live migration, high availability, and Shielded VMs for extra security.
It integrates tightly with Active Directory and PowerShell, making it especially attractive for IT teams already managing a Microsoft environment. Hyper-V Replica offers built-in disaster recovery, while clustering and failover support provide strong resiliency for production workloads.
It’s also a natural fit for hybrid setups, pairing well with Azure for cloud bursting, backup, or DR. As a VMware alternative, it stands out for organizations looking to consolidate costs and avoid new licensing complexities without sacrificing core virtualization capabilities.
What You Get
- Seamless integration with Microsoft tools like Active Directory, System Center, and PowerShell.
- Virtual networking and storage that rival VMware’s capabilities.
- Strong hybrid cloud integration with Azure.
Cost
It’s included with Windows Server licenses. Standard edition gives you 2 VMs per host, Datacenter edition offers unlimited. No separate hypervisor license means big savings if you’re a Windows shop.
Pros
- Cost-effective if you’re already using Windows Server.
- Familiar for Windows admins.
- Strong Azure integration for hybrid cloud.
- Robust security features.
Cons
- Weaker support for non-Windows OSes.
- Smaller third-party ecosystem than VMware.
- Some advanced networking features don’t match VMware’s NSX.
Example Use Case
Imagine you’re a mid-sized retailer with 200 employees, running Windows Server and Azure. Hyper-V lets you virtualize your ERP and inventory systems, saving on VMware licenses while using Azure for disaster recovery.
Best For
Windows-centric SMBs and enterprises eyeing hybrid cloud setups.
How HorizonIQ Can Help
HorizonIQ has years of experience managing Windows infrastructure. While we do not offer a managed Hyper-V solution, our team can set up the underlying infrastructure, install Windows, and make any ongoing patches. We have helped a number of companies use this model to successfully migrate from VMware to Hyper-V.
2. Proxmox VE
If you want flexibility without the price tag, Proxmox VE is worth a look. This open-source platform, built on Debian Linux, combines KVM VMs and LXC containers in an easy-to-use web interface.
It includes enterprise-grade features like live migration, high availability, backup scheduling, and built-in clustering, without separate licensing costs. Storage is equally flexible, with native support for ZFS, Ceph, and directory-based storage.
You can manage everything from a single pane of glass, and the REST API makes automation straightforward. As a VMware alternative, Proxmox appeals to teams that want full control over their stack, a strong open-source community, and the freedom to run mixed workloads with minimal overhead.
What You Get
- Intuitive web UI for managing VMs and containers.
- Clustering, live migration, and high availability.
- Built-in Ceph storage and backup scheduling.
Cost
It’s free, with optional support subscriptions (a few hundred bucks per socket annually), saving you up to millions compared to VMware.
Pros
- No licensing fees, all features included.
- User-friendly web interface.
- Supports both VMs and containers.
- Active community with frequent updates.
Cons
- Community support unless you pay for a subscription.
- Less polished UI than VMware.
- Smaller third-party ecosystem.
- Advanced features need Linux expertise.
Example Use Case
If you’re running IT for a university, Proxmox lets you manage Windows VMs for administrative apps and Linux containers for research microservices, slashing licensing costs.
Best For
SMBs, labs, and mixed-workload environments with Linux know-how.
How HorizonIQ Can Help
HorizonIQ was the first US infrastructure provider to offer a managed Proxmox private cloud solution. If you think Proxmox will work for your business but are worried that your team does not have the skills to manage the environment, this is the solution for you. HorizonIQ’s team does the heavy lifting and manages the setup and ongoing operation of the Proxmox cluster so your team can focus on more important tasks.
Looking to migrate without overlap costs?
Migration shouldn’t drain your budget. With HorizonIQ’s 2 Months Free, you can move workloads, skip the overlap bills, and gain extra time to switch providers without double paying.
Get 2 Months Free3. Nutanix AHV
If you’re looking to streamline infrastructure, Nutanix’s Acropolis Hypervisor (AHV) is a Type-1 hypervisor built into its hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) platform, managed via the Prism UI. AHV is tightly integrated with Nutanix’s storage, networking, and virtualization stack, enabling simplified management and automation from a single console.
It supports features like live migration, high availability, and integrated backup, while eliminating the need for separate hypervisor licensing. Prism Central provides policy-based management, capacity planning, and performance monitoring, making it appealing to IT teams looking to consolidate operations.
As a VMware alternative, AHV is best suited for organizations adopting HCI that want an all-in-one solution to reduce complexity and total cost of ownership.
What You Get
- One-click operations for upgrades and management.
- High availability, live migration, and integrated storage.
- Microsegmentation and hybrid cloud support.
Cost
Included with Nutanix HCI subscriptions, so no separate hypervisor fees, potentially lowering your total cost.
Pros
- Simplified infrastructure management.
- High performance and scalability.
- No separate hypervisor cost.
- Cloud-like management experience.
Cons
- High initial hardware investment.
- Potential Nutanix ecosystem lock-in.
- Fewer advanced features than VMware.
- Requires training for optimal use.
Example Use Case
If you’re a financial services firm replacing aging VMware and SAN setups, Nutanix AHV consolidates compute and storage and cuts down on VMware licensing costs.
Best For
Enterprises that are looking for HCI and simplified management, especially during hardware refreshes.
How HorizonIQ Can Help
HorizonIQ can work with you to potentially source Nutanix-compliant hardware. If that’s feasible, your team would be responsible for licensing and installing Nutanix.
4. XCP-ng
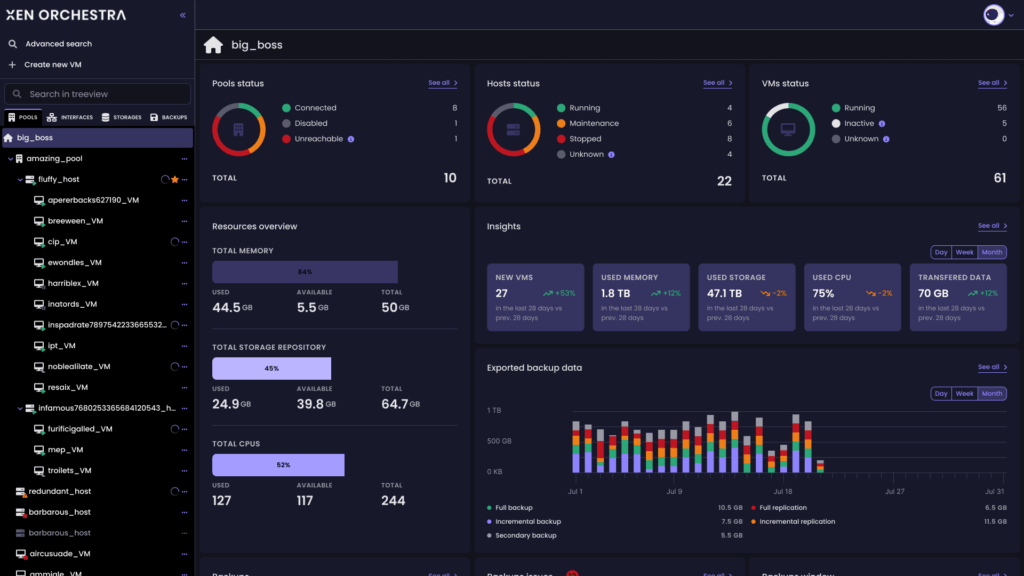
If you love VMware’s management style but hate the cost, XCP-ng is a free, Xen-based fork of XenServer.
It pairs with Xen Orchestra for a vSphere-like management experience. You get features like live migration, snapshots, high availability, and built-in backup and restore, which are all accessible through a clean, browser-based UI. XCP-ng supports both Windows and Linux VMs, and its active open-source community helps with regular updates and plugin development.
It’s also API-friendly, making it a good fit for teams looking to automate provisioning and lifecycle management. As a VMware alternative, it offers familiar functionality without vendor lock-in, making it appealing for organizations prioritizing transparency and long-term cost savings.
What You Get
- Live migration (XenMotion), high availability, and snapshots.
- GPU virtualization support.
- Xen Orchestra’s polished, vCenter-like web UI.
Cost
Free, with optional Vates support, making it a fraction of VMware’s cost.
Pros
- Free and open-source.
- Familiar management for VMware admins.
- Robust Xen hypervisor.
- Active community development.
Cons
- Less mindshare than KVM or Hyper-V.
- Fewer third-party integrations.
- Windows VM tools aren’t as seamless.
- Some Xen-specific learning required.
Example Use Case
If you’re a managed service provider, XCP-ng lets you host client workloads with Xen’s multi-tenant isolation and Xen Orchestra’s intuitive management, replacing VMware clusters.
Best For
Mid-sized enterprises and MSPs that want a VMware-like experience without the price tag.
How HorizonIQ Can Help
HorizonIQ can set up the necessary infrastructure for you to run XCP-ng. From here, your team would install the XCP-ng image and get it going.
5. Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
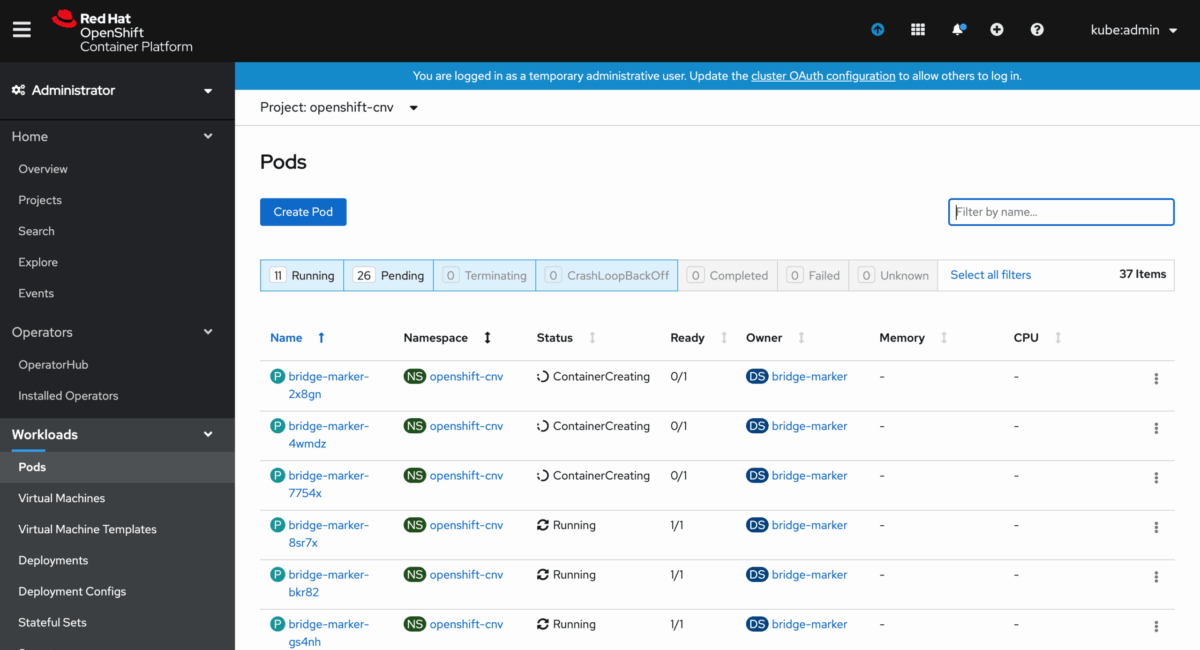
If you’re modernizing Linux workloads, OpenShift Virtualization extends your Red Hat stack with container-native VMs. It builds on OpenShift and KVM, with automation powered by Ansible and RHEL integration.
You can run VMs alongside containers on the same Kubernetes platform, making it easier to manage hybrid workloads and transition legacy apps. Built-in features include live migration, high availability, and persistent storage via OpenShift Data Foundation.
Developers can manage VMs using the same GitOps and CI/CD workflows they use for containers, streamlining operations across teams. As a VMware alternative, it’s a strong choice for Red Hat environments looking to unify VM and container management under a single, cloud-native control plane.
What You Get
- Run virtual machines alongside containers.
- Live migration, snapshots, and persistent storage.
- Unified management through the OpenShift web console.
Cost
Subscription-based, often more affordable than VMware, especially if you already use OpenShift or Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
Pros
- Integrated with RHEL, OpenShift, and Ansible.
- Ideal for hybrid container and VM environments.
- Strong security and Red Hat support.
- Future-ready Kubernetes-native architecture.
Cons
- Requires OpenShift knowledge to manage.
- More complex than traditional hypervisors.
- Limited to KVM-based VMs.
- Still maturing compared to legacy virtualization tools.
Example Use Case
A fintech company runs OpenShift for cloud-native apps and adds OpenShift Virtualization to support legacy VMs without expanding infrastructure.
Best For
Enterprises running Linux and containers who are looking to consolidate VMs into a Kubernetes-native platform.
How HorizonIQ Can Help
HorizonIQ has years of experience managing Red Hat infrastructure. While we do not offer a managed OpenShift solution, our team can set up the underlying infrastructure, install your desired version of Red Hat, and make any ongoing patches.
6. OpenStack
If vendor lock-in and licensing costs are top concerns, OpenStack offers a compelling alternative. This open-source cloud platform, governed by the Open Infrastructure Foundation, is vendor-agnostic and designed to run on standard hardware.
Built to support hyper-converged architectures, OpenStack combines compute, networking, and storage (often with Ceph) into a unified solution. As a VMware alternative, OpenStack offers full control over your private cloud infrastructure, free from proprietary constraints, and is backed by a global community with zero licensing fees.
What You Get
- Open-source cloud infrastructure platform (Apache-licensed).
- Vendor-agnostic deployment on standard hardware.
- Hyper-converged architecture with integrated compute, networking, and storage.
- Native Ceph support for scalable storage.
- Active global support community.
- No vendor lock-in or proprietary dependencies.
Cost
OpenStack itself is free (no licensing fees, no per-core or per-socket pricing). Costs center around your hardware, staffing, and support resources. Compared to VMware’s subscription-based model, OpenStack can drastically reduce software-related expenses.
Pros
- No software licensing costs.
- Total control over infrastructure.
- Avoids vendor lock-in.
- Large, active open-source community.
- Supports scalable private cloud deployments.
Cons
- Complex to deploy and manage without in-house expertise.
- Community-based support unless working with a managed provider.
- Frequent updates can require careful version management.
- May require external consultants or additional staff.
Example Use Case
Enterprises like Target and GE Healthcare use OpenStack to avoid long-term vendor commitments while controlling cloud costs. By deploying OpenStack on standard servers, IT teams can build private cloud environments without licensing fees and scale workloads flexibly using Ceph for storage.
Best For
Enterprises, large organizations, and teams prioritizing vendor neutrality, cost control, and infrastructure ownership.
How HorizonIQ Can Help
HorizonIQ can provision the underlying hardware and networking needed to deploy OpenStack. From there, your team can install and configure Harvester to manage VMs and containers in your environment.
7. Harvester

If simplicity and Kubernetes-native management are priorities, Harvester offers a modern, open-source alternative to VMware. Built by SUSE, Harvester is a lightweight hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) platform that combines virtualization and Kubernetes orchestration into a unified solution.
Using KVM as its underlying hypervisor and Rancher for cluster management, Harvester allows IT teams to manage both virtual machines and containers through a single, web-based interface. As a VMware alternative, Harvester eliminates hypervisor licensing costs and simplifies virtualization with built-in storage, networking, and monitoring.
What You Get
- Open-source HCI platform (Apache-licensed).
- Integrated KVM-based hypervisor.
- Kubernetes-native VM management via Rancher UI.
- Built-in Longhorn block storage and integrated virtual networking.
- Lightweight deployment on standard x86 hardware.
- No proprietary software dependencies.
- SUSE support available (optional).
Cost
Harvester is fully open-source with no licensing fees. You only pay for hardware and optional SUSE support. Compared to VMware’s subscription-based pricing, Harvester offers significant savings by eliminating hypervisor and management licensing.
Pros
- No hypervisor licensing costs.
- Simple, unified VM and container management.
- Kubernetes-native architecture (ideal for modern workloads).
- Lightweight, fast deployment.
- Integrated storage and networking reduce third-party dependencies.
- Backed by SUSE with optional enterprise support.
Cons
- Less mature than OpenStack or VMware in large-scale enterprise deployments.
- Smaller ecosystem and community.
- Limited advanced networking features compared to NSX.
- Focused more on edge, SMB, and modern workloads than legacy enterprise apps.
Example Use Case
SMBs and DevOps teams use Harvester to simplify virtualization without sacrificing flexibility. For example, a software company might deploy Harvester across 5–10 servers, managing VMs for backend services while simultaneously orchestrating container workloads via Rancher.
Best For
- SMBs, SaaS providers, and DevOps teams seeking a Kubernetes-native virtualization platform.
- Organizations prioritizing simple HCI deployment, modern workload management, and reduced licensing costs.
How HorizonIQ Can Help
HorizonIQ can provision the underlying hardware and networking needed to deploy Harvester. From there, your team can install and configure Harvester to manage VMs and containers in your environment. If needed, HorizonIQ can assist with initial setup guidance to help accelerate your deployment.
8. XenServer
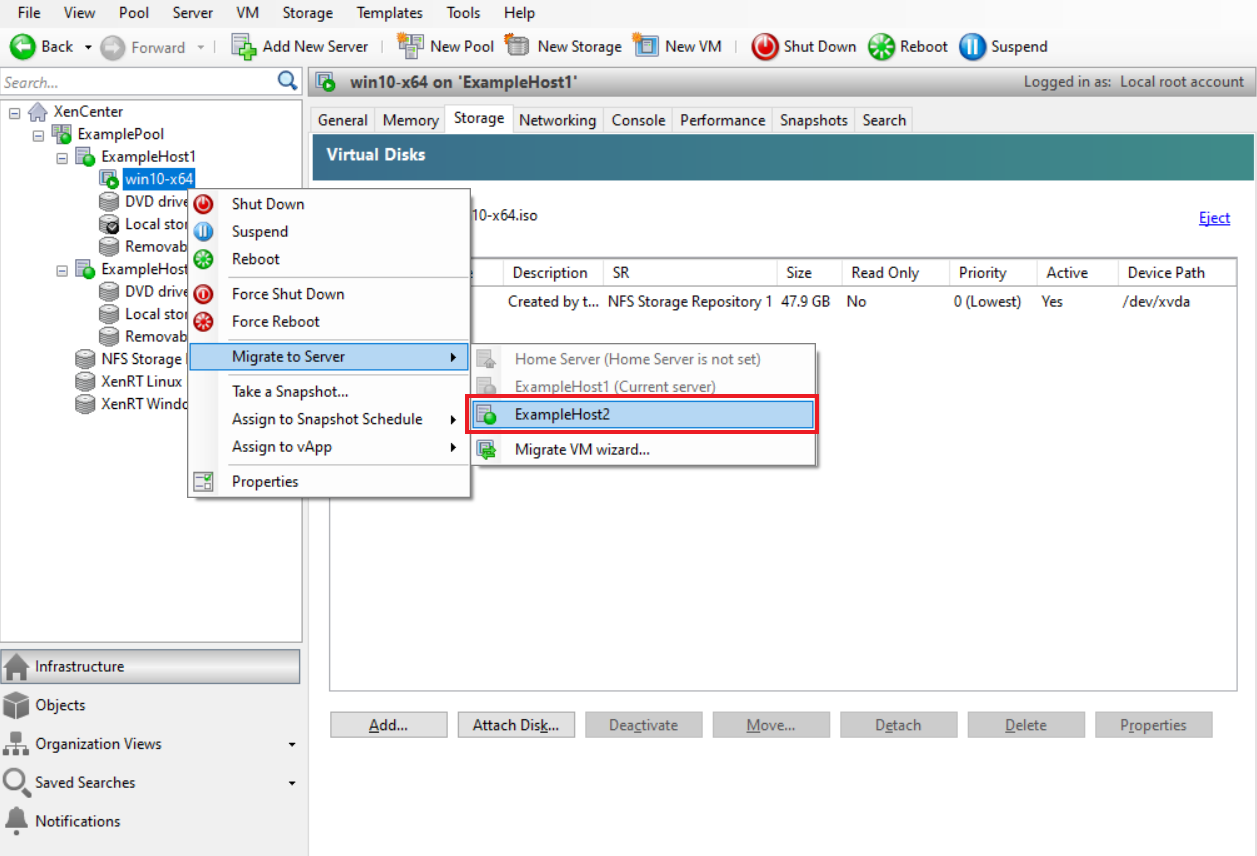
If virtual desktops are your priority, XenServer 8.4 (formerly known as Citrix Hypervisor) is a Xen-based Type-1 hypervisor purpose-built for VDI and GPU-intensive workloads. It integrates tightly with Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, making it a strong fit for Citrix-centered environments.
Features like GPU passthrough, high availability, and live migration are built in, along with security tools like Direct Inspect APIs for introspection. XenServer is optimized for scalability, supporting large hosts and dense VM deployments—ideal for desktop virtualization at scale.
As a VMware alternative, it stands out in environments that prioritize graphics performance and Citrix integration, especially where cost and licensing simplicity are key concerns.
What You Get
- High availability, live migration (XenMotion), and GPU virtualization
- Security features like Direct Inspect APIs
- Optimized performance for graphics-rich and multi-user desktop workloads
Cost
Free base version, with paid editions for premium features—generally cheaper than VMware.
Pros
- Purpose-built for Citrix VDI
- Strong GPU virtualization and security features
- Cost-effective alternative to VMware
- Stable, mature Xen-based architecture
Cons
- Smaller ecosystem and mindshare.
- Fewer advanced features than VMware.
- Dependency on Citrix ecosystem.
- Windows-only XenCenter GUI.
Example Use Case
If you’re a healthcare provider delivering GPU-accelerated virtual desktops for 3D imaging, XenServer integrates seamlessly with Citrix VDI, saving costs.
Best For
Enterprises with Citrix VDI or security-focused workloads.
How HorizonIQ Can Help
HorizonIQ can setup the necessary infrastructure for you to run XenServer. From here, your team would install the XCP-ng image and get it going.
9. SUSE Linux Enterprise
If you’re in a SUSE-centric environment, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) supports KVM and Xen hypervisors, offering flexibility for Linux-heavy workloads. It includes built-in tools for VM lifecycle management, live migration, and high availability, all managed through YaST and SUSE Manager.
SLES also integrates with Rancher for container orchestration, making it a solid option for hybrid environments. As a VMware alternative, it’s ideal for enterprises standardized on SUSE looking to consolidate virtualization and container infrastructure under one support umbrella.
What You Get
- KVM/Xen support with virt-manager GUI.
- SR-IOV and Secure Boot for performance and security.
- Integration with Rancher for VM/container workflows.
Cost
Subscription-based, competitive with VMware for large deployments.
Pros
- Flexible KVM/Xen options.
- Enterprise-grade stability.
- Cost-effective for SUSE users.
- No per-core licensing.
Cons
- No polished centralized management.
- Smaller user base.
- Less optimized for Windows.
- Requires Linux expertise.
Example Use Case
If you’re a manufacturing firm running SAP HANA, SLES with KVM leverages your existing SUSE subscriptions for virtualization.
Best For
SUSE-based enterprises with Linux expertise.
How HorizonIQ Can Help
HorizonIQ can set up the necessary infrastructure for you to run SUSE Linux Enterprise. From here, your team would install SUSE Linux Enterprise and get it going.
10. Oracle VirtualBox
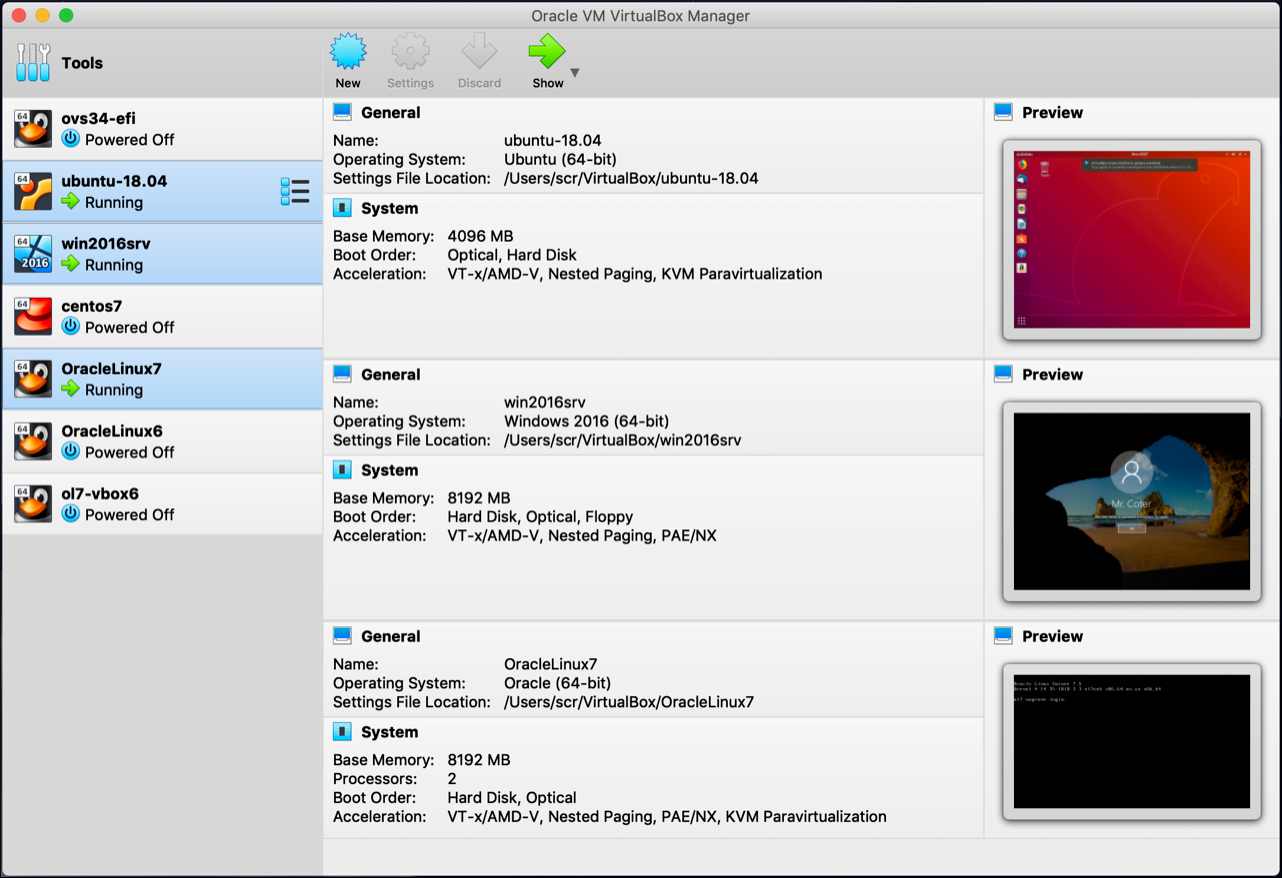
If you need simple, small-scale virtualization, VirtualBox is a free, Type-2 hypervisor for desktops and servers. It is also well-suited for non-production environments.
While it lacks enterprise features like clustering or live migration, it’s a reliable tool for testing, training, and local development. As a VMware alternative, it’s best for individual users or teams needing lightweight VM support without infrastructure overhead.
What You Get
- User-friendly GUI for VM creation.
- Snapshots, clones, and shared folders.
- Supports multiple OSes with paravirtualization.
Cost
Free, with an optional commercial Extension Pack for enterprises.
Pros
- Free and easy to use.
- Cross-platform versatility.
- Great for dev/test environments.
- No dedicated server needed.
Cons
- Not suited for production.
- Performance overhead is Type-2.
- Limited support and scalability.
Example Use Case
If you’re a software developer, VirtualBox lets you test applications across multiple OSs on your laptop to avoid VMware Workstation costs.
Best For
Developers, labs, and small-scale virtualization.
How HorizonIQ Can Help
HorizonIQ can set up the necessary infrastructure for you to run VirtualBox. From here, your team would install VirtualBox and get it going.
What Are the Best VMware Alternatives Based On Company Size?
Small Businesses
Select Proxmox VE for open-source flexibility and control, or Hyper-V in case you are a Windows shop. VirtualBox is suitable for small non-production environments like dev/test.
Mid-Sized Businesses
Consider Hyper-V on Windows servers, Proxmox VE for open-source clusters, or Nutanix AHV for simplified HCI management. XCP-ng is also a solid option to minimize licensing costs.
Large Enterprises
Employ a multi-hypervisor strategy. Utilize Nutanix AHV or Hyper-V for infra core workloads, OpenStack for scale-out private cloud, and Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization or SUSE Linux Enterprise for Linux-dominant workloads. Deploy XenServer in Citrix VDI environments where necessary.
Does Proxmox Meet Enterpise Needs as a VMware Alternative?
Proxmox is no longer just for home labs. What started as an open-source project has matured into a reliable, flexible, and production-grade hypervisor stack adopted by organizations of all sizes, from startups to nationwide retailers and engineering firms managing GPU workloads.
Enterprise users consistently report that Proxmox “just works.” Whether in 3-node clusters or sprawling 17-host, multi-site deployments with 400+ VMs and Ceph-backed storage, it handles high availability (HA), clustering, and live migrations with ease.
Some even refer to the stack as “self-healing” when paired with Ceph. Proxmox is also known for its resilience. One Reddit user noted the platform recovered completely from a failed Ceph node without any VM downtime.
Proxmox also integrates well with Veeam Backup solutions to enable enterprise-grade backup and disaster recovery strategies. Administrators can leverage Veeam’s backup scheduling, instant recovery, and replication features to protect Proxmox virtual machines while gaining data integrity and minimizing downtime even during critical failures.
Cost Savings Without Compromising Functionality
Proxmox eliminates hypervisor licensing costs while offering features comparable to vSphere, including. One enterprise cited a $2.3 million VMware licensing quote they avoided by switching.
Storage & Backup Options That Work
Proxmox integrates well with enterprise storage options like Starwind VSAN, Ceph, iSCSI, and NFS. Users run clusters on shared NetApp storage and Cisco UCS blades without issue. Meanwhile, Proxmox Backup Server offers high deduplication, easy offsite sync (even to S3 or AWS), and native VM and container backups (often cited as “zero-budget” DR for small teams).
Performance & Flexibility
Compared to ESXi, many users find Proxmox faster and more resource-efficient. Linux-native tools, live migration, and RESTful APIs support automation with Ansible and Terraform. Though it lacks a polished vSphere/vCenter equivalent, many are scripting and automating day-to-day tasks to reduce tech debt and maintenance overhead.
What Are the Next Steps When Choosing a VMware Alternative?
The virtualization landscape in 2025 gives you plenty of options to move away from VMware, while balancing cost, simplicity, and your strategic goals.
Open-source picks like Proxmox and XCP-ng cut licensing fees, Hyper-V leverages your Microsoft ecosystem, Nutanix AHV simplifies HCI, and cloud VDI like Ace Cloud supports remote work. Here’s how to get started:
- Inventory Your Workloads: List your current workloads and pain points with VMware.
- Test Alternatives: Try a free trial of Proxmox or Hyper-V on non-critical systems to see what fits.
- Assess Training and Support: Check what skills your team needs and what vendor support is available.
- Plan a Phased Migration: Move gradually to minimize risk.
If you’re weighing multiple options, I recommend engaging with user communities like Reddit, running trials, and measuring performance to find your best fit. You can also partner with a neutral managed infrastructure provider, like HorizonIQ, that can help you pilot and compare setups without committing upfront.
By diversifying your virtualization strategy, you’ll cut costs, boost flexibility, and future-proof your IT infrastructure with modern VMware alternatives.
Explore HorizonIQ's
Managed Private Cloud
LEARN MORE
Stay Connected

What Is Hybrid Cloud Architecture?
Hybrid cloud architecture refers to an IT infrastructure setup that combines private cloud, public cloud, and sometimes on-prem environments, integrated to work as a single, cohesive system. It gives organizations the flexibility to run workloads in the most appropriate environment while enabling seamless data and workload portability.
At its core, hybrid cloud architecture is about balancing control and scalability. Businesses can keep sensitive data and mission-critical workloads in secure, single-tenant environments while using public cloud services to scale up quickly or support less-sensitive workloads. This blend allows for cost optimization, regulatory compliance, and infrastructure agility.
Why Is Hybrid Cloud Architecture Important in 2025?
As of 2025, over 84% of companies use at least one private cloud, and more than 32% of enterprise workloads run in private environments. With rising concerns around cloud spend, data sovereignty, and AI infrastructure needs, hybrid cloud offers a future-proof path forward.
Gartner predicts cloud services will become a business necessity by 2028, but not all workloads are fit for hyperscaler public clouds. Hybrid cloud architecture enables businesses to:
- Achieve cost predictability and control
- Optimize for performance with low-latency infrastructure
- Maintain compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and SOC 2
- Scale AI, analytics, and edge workloads with dedicated GPU-powered private environments
How Does Hybrid Cloud Architecture Work?

Hybrid cloud architecture works by connecting multiple environments, such as a managed private cloud (like HorizonIQ), public cloud endpoints (AWS, Azure, GCP), and sometimes on-prem data centers, via secure networking and orchestration layers.
Key components include:
- Private Cloud Infrastructure: Single-tenant infrastructure that offers dedicated resources, compliance, and predictable performance.
- Public Cloud Integration: Enables elasticity and scale, which is ideal for burst workloads or experimentation.
- Networking Layer: Includes cloud on-ramps, cross-connects, and SD-WAN to provide fast, secure data transfer between environments.
- Management and Orchestration Tools: Tools like HorizonIQ Compass unify visibility, cost control, and performance monitoring across environments.
What Are the Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Architecture?
Hybrid cloud brings together the best of both worlds. Some key benefits include:
- Flexibility: Run each workload in the most appropriate environment.
- Cost Optimization: Keep predictable workloads in private cloud to avoid surprise bills.
- Security and Compliance: Use single-tenant infrastructure to isolate sensitive data and meet regulatory standards.
- Scalability: Burst into the public cloud during seasonal spikes or AI training runs.
- Resilience: Architect for failover and disaster recovery across environments.
What’s the Difference Between Hybrid Cloud and Multicloud?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, hybrid cloud and multicloud represent different strategies.
- Hybrid Cloud: Focuses on integration between private and public cloud environments. Workloads can move between them as needed.
- Multicloud: Involves using services from multiple public cloud providers (e.g., AWS + GCP), often without deep integration.
In short: Hybrid cloud = integration. Multicloud = diversification.
HorizonIQ specializes in hybrid architectures because they offer more control, cost efficiency, and resilience, especially when managed through a centralized platform.
What Industries Benefit Most from Hybrid Cloud Architectures?
Hybrid cloud architecture is ideal for industries that need both control and flexibility:
Industry |
Use Case |
Healthcare |
Host electronic health records (EHRs) on-prem or in a secure private cloud while using public cloud for analytics. |
Financial Services |
Meet PCI DSS and SOC 2 requirements while enabling innovation with AI-powered tools. |
Gaming |
Combine low-latency bare metal with cloud-based scaling for traffic spikes. |
Media & Entertainment |
Process and store large volumes of content with performance and control. |
Government & Legal |
Maintain air-gapped, compliant environments while enabling modern workflows. |
How Does HorizonIQ Strengthen Hybrid Cloud Capabilities?
HorizonIQ’s hybrid cloud platform goes beyond basic integration—it’s designed for intelligent workload management, performance scaling, and operational control:
- Workload Placement Control: HorizonIQ Hybrid Cloud lets you run predictable, steady workloads on flat-rate private infrastructure to control costs. When demand spikes, workloads can automatically burst into AWS, Azure, or GCP using HorizonIQ’s load balancer. You can define maximum connection thresholds, and when exceeded, overflow traffic is routed to public cloud targets. Alternatively, workload orchestration can be handled using infrastructure as code or public cloud auto-scaling policies.
- AI-Ready Infrastructure: For machine learning and AI development, HorizonIQ enables training on public cloud GPUs with cost-effective inference running on dedicated, secure private infrastructure. Our environments are fully compatible with lightweight and local models, supporting fast iteration and stable deployment.
- Real-Time Traffic Spike Scalability: The architecture supports elastic scaling to public cloud in real time without impacting uptime or performance. Thanks to low-latency interconnects and a 100% uptime SLA, your applications remain responsive even during peak usage.
- Security & Compliance: Sensitive workloads run on single-tenant, private infrastructure with full data isolation, while less critical tasks can burst into the public cloud. This allows you to maintain compliance (HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOC 2) without extending audit scopes unnecessarily.
- Container Support: HorizonIQ’s Proxmox-based infrastructure natively supports containers and Kubernetes, making it easy to deploy modern workloads in hybrid environments.
- Flexible Deployment Models: Choose between a fully self-managed environment or let HorizonIQ manage your entire hybrid setup. This flexibility suits a wide range of technical teams and resourcing levels.
Is Hybrid Cloud Architecture Right for Your Business?
If your organization needs more control, better performance, and improved cost visibility (but still wants the flexibility of public cloud), hybrid cloud architecture could be your answer.
HorizonIQ makes it easy to architect, deploy, and manage a hybrid environment tailored to your business goals. Whether you’re modernizing legacy apps, scaling AI infrastructure, or navigating compliance frameworks, we’re here to help.
Ready to build a resilient hybrid cloud architecture? Contact us to explore the possibilities.
Explore HorizonIQ's
Managed Private Cloud
LEARN MORE
Stay Connected

Network Connectivity: From Cross‑Connects to Cloud On‑Ramps with HorizonIQ Connect
Why Does Network Connectivity Matter More Than Ever?
With 98% of enterprises adopting a multicloud strategy and 83% planning to use multicloud interconnection, the ability to connect disparate cloud environments seamlessly has become a critical driver of infrastructure resilience.
Poor connectivity can lead to sluggish performance, skyrocketing costs, and security vulnerabilities that jeopardize operations.
For these reasons, we’re exploring why robust network connectivity is essential, the challenges businesses face, and how solutions like HorizonIQ Connect can transform your hybrid and multicloud ecosystem.
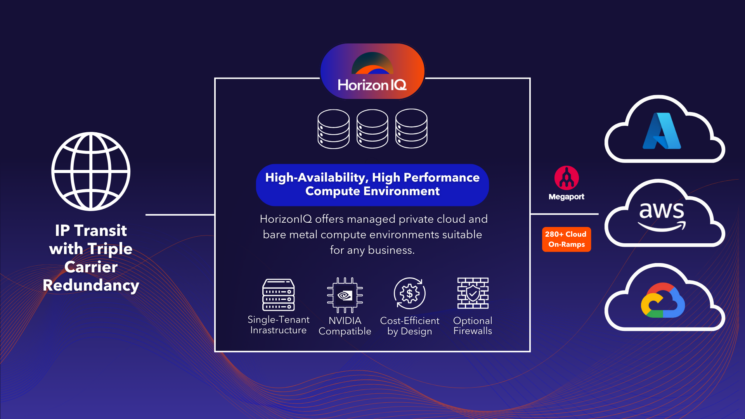
Why Is Network Connectivity Key to Multicloud Success?
Imagine a global e-commerce platform where AI analytics on Microsoft Azure struggle to sync with a customer-facing app on AWS, thereby delaying responses and frustrating users.
This scenario is all too common in multicloud environments. As businesses increasingly rely on distributed IT environments (e.g., running AI workloads on Google Cloud, databases on Azure, and frontends on AWS), robust connectivity is non-negotiable.
Connectivity is now a factor that determines whether businesses can deliver fast, secure, and cost-effective services. Poor connectivity leads to:
- Lost Revenue: Latency can disrupt user experiences, with studies showing that a 100ms delay in website load time can reduce conversion rates by 7%.
- Escalating Costs: Unoptimized data transfers, such as cloud egress fees, can inflate budgets by up to 30% annually.
- Security Risks: Public internet connections expose sensitive data.
What Are the Key Challenges in Network Connectivity?
Multicloud and hybrid cloud architectures offer flexibility, but they introduce significant complexity. Here are the primary connectivity challenges organizations face, and how to overcome them:
1. Latency and Performance Variability
Geographically dispersed cloud resources often lead to inconsistent performance. Real-time applications, such as video streaming or financial trading platforms, suffer when data travels across regions, with latency spikes impacting user satisfaction.
Solution: Deploy private, high-speed connections like cloud on-ramps or Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to bring data closer to end-users. Edge computing can further reduce latency by processing data locally.
2. Cost Overruns and Hidden Fees
Cloud egress fees and redundant infrastructure can silently drain budgets. Organizations often face unpredictable costs when transferring data between clouds or maintaining underutilized resources.
Solution: Use direct interconnects to minimize egress fees. Centralized cost management tools provide visibility into usage and help organizations eliminate wasteful spending.
3. Security and Compliance Risks
Multicloud environments expand the attack surface. Public internet connections increase exposure to cyber threats, and varying compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA, PCI-DSS) across providers complicate governance.
Solution: Implement private, encrypted connections and unified security policies via platforms like HorizonIQ Connect. Regular audits and compliance-ready providers ensure data protection across clouds.
4. Management Complexity
Each cloud provider has unique tools, APIs, and dashboards, making centralized management a nightmare.
Solution: Adopt multicloud management platforms that unify monitoring, orchestration, and automation. Tools like HorizonIQ’s Compass portal and Megaport’s API simplify oversight and streamline operations.
What Are the Options for Network Connectivity?
To address network connectivity challenges, businesses can choose from several connectivity models, each with distinct trade-offs. Here’s a detailed comparison:
- VPN Tunnels via Public Internet
- Pros: Quick to set up, cost-effective for small-scale or testing environments.
- Cons: Unreliable performance, high latency, and security risks over public networks.
- Best for: Temporary or low-stakes workloads with minimal data transfer needs.
- Data Center Cross-Connects
- Pros: Offers dedicated, low-latency connections (e.g., AWS Direct Connect, Azure ExpressRoute) with predictable costs.
- Cons: High upfront costs (CapEx) and limited flexibility for scaling across multiple clouds.
- Best for: Enterprises with stable, high-performance workloads in a single cloud.
- Cross-Cloud Interconnects
- Pros: Private peering between clouds (e.g., AWS ↔ GCP) reduces latency and egress fees while enhancing security.
- Cons: Static configurations and provider-specific limitations can hinder multicloud flexibility.
- Best for: Organizations with consistent workloads across two major cloud providers.
- Network as a Service (NaaS) with Cloud On-Ramps
- Pros: Software-defined, scalable, and secure connections with rapid provisioning.
- Cons: Dependency on provider coverage and potential learning curve for integration.
- Best for: Dynamic, multicloud environments with bursty workloads or global reach.
How Do Physical vs Virtual Cloud Cross‑Connects Compare?
- Physical (Layer 1): Dedicated links to a single cloud provider are reliable but costly and inflexible for multicloud setups.
- Virtual (Layer 2): A single port connects multiple clouds via virtualized networks, reducing costs and complexity. HorizonIQ’s Connect, paired with Megaport’s virtual routing, excels in this model.
Why Should You Choose HorizonIQ Connect for Network Connectivity?
HorizonIQ, in partnership with Megaport, offers a game-changing approach to multicloud and hybrid cloud connectivity. Our solutions address the challenges above with flexibility, performance, and cost-efficiency. Here’s why they stand out:
Key Features
- Rapid Provisioning: Spin up private connections to AWS, Azure, or GCP in minutes, not weeks, via Megaport’s Software Defined Network (SDN).
- Cost Savings: Reduce data transfer costs by up to 70% compared to public cloud providers, thanks to optimized on-ramps and pay-as-you-go pricing.
- Global Reach: With nine regions and access to over 280 cloud providers, HorizonIQ Connect provides low-latency connections worldwide.
- Security and Compliance: Certified for ISO-27001, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and SOC 2, HorizonIQ Connect provides secure, compliant connections.
- Unified Management: HorizonIQ’s Compass portal and Megaport’s API offer a single interface for monitoring, scaling, and managing multicloud networks.
How Do I Choose the Right Network Connectivity Strategy?
Selecting the best approach depends on your business needs. Consider these questions:
- Performance Needs: Do you require ultra-low latency? Opt for private interconnects or NaaS with cloud on-ramps.
- Workload Dynamics: Are workloads bursty or seasonal? NaaS offers flexibility, while cross-connects suit static needs.
- Compliance Requirements: Handling sensitive data? Choose private links and providers with certifications like PCI-DSS.
- Budget Model: Prefer predictable costs? Dedicated cross-connects work well. Need flexibility? NaaS and pay-as-you-go models are ideal.
- Management Needs: Want centralized control? Platforms like HorizonIQ’s Compass and Megaport’s API simplify multicloud oversight.
Getting Started with HorizonIQ Connect
To build a future-proof multicloud network, follow these steps:
- Assess Needs: Evaluate workloads, performance goals, compliance requirements, and budget constraints. Choose from both fully managed and self-managed options.
- Choose a Model: Test VPNs for small-scale needs, cross-connects for stable workloads, or NaaS for dynamic multicloud setups.
- Partner with HorizonIQ: Engage with HorizonIQ to design a tailored connectivity solution, leveraging our Connect service and Megaport’s SDN.
- Pilot and Scale: Start with a pilot connecting one or two clouds to measure latency and costs, then expand to full production with redundancy and automation.
- Monitor and Optimize: Use HorizonIQ’s Compass portal and Megaport’s API for real-time insights and policy adjustments.
Build a Competitive Edge with HorizonIQ Connect
In a hybrid and multicloud world, connectivity isn’t just a technical necessity—it’s a strategic advantage. Poor connections can cripple innovation, inflate costs, and expose vulnerabilities, while optimized networks drive performance, savings, and growth.
HorizonIQ and Megaport deliver a powerful solution by combining rapid provisioning, global reach, and robust security to empower businesses.
Don’t let connectivity hold you back. Contact HorizonIQ to build a high-performance, secure multicloud network tailored to your needs.




